Country Name: South Sudan
Official Name: Republic of South Sudan
News Category: New Countries
Summary: The Republic of South Sudan has officially declared independence from Sudan. The declaration comes within the legal framework of a 2005 peace agreement between the north and south, and as a result of a 2011 popular vote. South Sudan is expected to be rapidly accepted into the international community as the world's newest country.
History
Northern and Southern Sudan are historically distinct regions, both culturally and geographically. The arid north has long been dominated by nomadic Arab herders, with Islam as the primary religion. Meanwhile, the wetter south is populated by various agricultural peoples practicing local religions or Christianity. The north and south were ruled as separate colonies by the British during the first half of the 20th Century, but were later unified, with power weighted toward the north. By the time Sudan gained independence in 1956, a civil war was raging over the south's demands for greater representation and autonomy. A peace agreement was finally reached in 1972, granting Southern Sudan many of its demands; but the country descended again into war in 1983, after the central government in Khartoum withdrew the concessions.
Wikipedia: History of South Sudan
 |
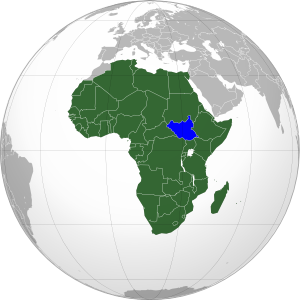
Newly independent South Sudan in purple. Sudan in
green. Modified from this map (license: CC BY-SA). |
Independence
The devastating second civil war finally came to an end with the 2005 Comprehensive Peace Agreement, signed by the Government of Sudan in the north and the Sudan People's Liberation Movement in the south. The agreement specified that the people of Southern Sudan would have the chance to vote on whether to become independent. After six years of uneasy coexistence between the two sides, the referendum was finally held in January 2011. Ninety-nine percent of voters chose independence, and the date for the declaration was set for July 9. Despite diplomatic confrontations and armed clashes, the separation proceeded, with the Government of Sudan in the north becoming the first country to recognize the south's independence. The north retained the name "Sudan".
 |
Former Sudan. South Sudan in blue. Green areas remain
part of Sudan (disputed regions in dark green). Disputed
Abyei (yellow) is under U.N. control. Modified from this
map by Wikimedia user Lokal_Profil (CC BY-SA 2.5). | |
However, the status of three border regions - the Abyei Area, South Kordofan state, and Blue Nile state - has not yet been decided. Abyei is claimed both by the south and by the north, which is in the process of turning it over to U.N. peacekeeping forces. The 2005 agreement promised Abyei's people the chance to vote on which side to join, but the referendum hasn't come together. South Kordofan and Blue Nile are controlled by the north, but were promised vaguely defined "popular consultations", which also have not come to pass, leading to continued violence in South Kordofan. The region of Darfur in western Sudan was not at issue in the north-south civil war, and remains part of the north.
 |
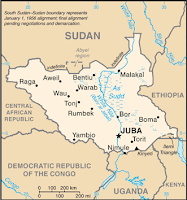
| South Sudan's capital and states. Modified from this map (public domain). |
Wikipedia: Southern Sudanese Independence Referendum
Country Profile
South Sudan is a land-locked country in East Africa, bordered by six other countries, and divided into ten states. It is a constitutional republic with its capital in the city of Juba, and is currently led by President Salva Kiir, a former southern rebel leader. Bisected by the White Nile river, the lushly vegetated country is home to some of the largest remaining populations of endangered African wildlife. South Sudan's roughly 8 million people come from a diverse range of cultural groups, the largest of which is the Dinka people. While English is the official language, Dinka and many other languages are spoken locally, and Arabic (the official language of Sudan) is also widely spoken as a second language. Although the country has rich oil resources, its people currently suffer with one of the lowest standards of living in the world.
Wikipedia: Republic of South Sudan
International Relations
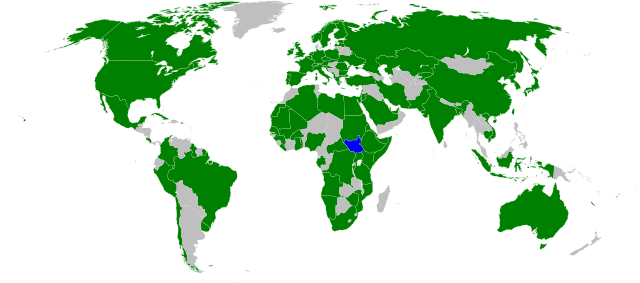
Technically, South Sudan is still a "partially recognized" state, as it has not yet been admitted to the United Nations and is still awaiting diplomatic recognition from many countries. However, it is expected to be admitted into the U.N. within days, and its recognition is growing rapidly: it has already been recognized by about 60 U.N. member countries and four other sovereign states. In addition to the U.N., South Sudan has applied for membership to the African Union, the Commonwealth of Nations, and the East African Community. It has been invited into the Arab League, but is not likely to join, as most of its people do not identify as Arabs (unlike Sudan in the north).
Political Geography Now will continue to publish updates as South Sudan's international status evolves.
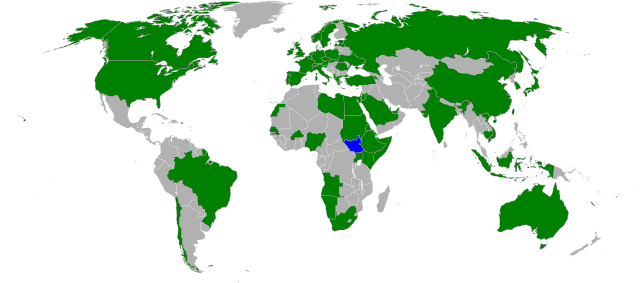 |
| Countries which have recognized South Sudan's sovereignty (green). South Sudan in blue. Modified from this Wikimedia map (public domain). |
Wikipedia: Foreign Relations of South Sudan