Country Name: Azawad
(English, Tuareg, French), Azawād (Arabic)
News Categories: New Countries,
Breakaway States,
Unrecognized States
Summary: Tuareg-led rebels in northern Mali have declared "the independent state of Azawad", after taking control of all of the region's major cities and military bases and advancing to near the edge of their claimed territory. Azawad is not recognized as an independent country by any U.N. members, making it an example of a so-called "breakaway state".
See Also: Mali Divided by Separatist Fighting;
all Mali map updates
MNLA Claims Independent Azawad
The National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad (MNLA) today
declared independence from Mali via a statement in French on its website.
The rebels of the MNLA, mostly from the Tuareg ethnic group of the Sahara Desert, claim that the northern region of Mali, which they call Azawad, was wrongly included in that country when it declared its independence from France in 1960. There has not yet been any announcement on what form of government Azawad will have, or on which city will be its capital, but the MNLA says it is committed to democracy, to following the rules of the U.N., and to respecting the borders of other countries in the region.
Full Text: Declaration of Independence of Azawad (English Translation)
The breakaway state of Azawad is not yet recognized diplomatically by any of the world's other countries, and is unlikely to be any time soon. It joins the ranks of the various wholly or partially unrecognized states of the world, including fellow African state
Somaliland, which similarly controls its whole territory despite complete lack of recognition from either the U.N. or other states. This status will likely prevent Azawad from appearing on mainstream world maps for some time to come.
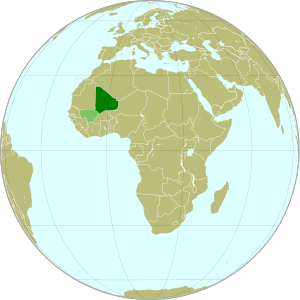 |
Azawad (dark green) and remainder of Mali (light green) in
Africa. Modified from this Wikimedia map (public domain). |
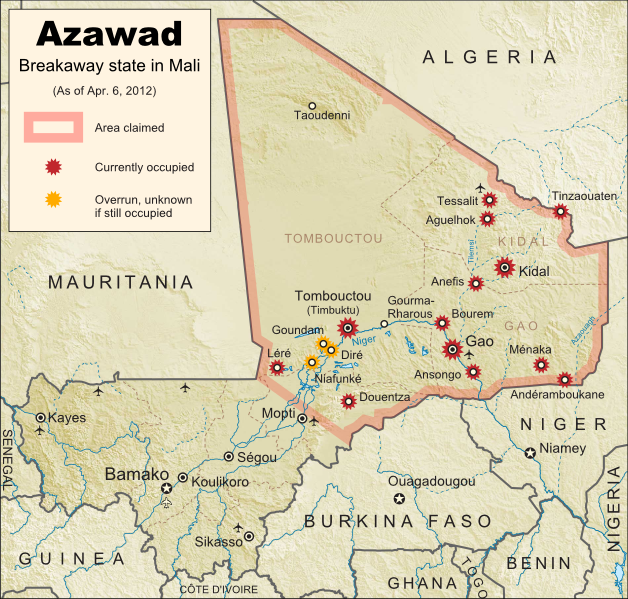
Update on Territorial Control
Since our
last map update,
the Tuareg rebels of the MNLA advanced as far as the town of Douentza (according to their own claims, which have not been disputed), after which they
declared a ceasefire, saying they had completed their mission to liberate Azawad. The town of Niafunké has also apparently switched hands a few times over the last few months (
source in French), with its current situation unclear. The reality is that the Malian military probably no longer controls anything within the claimed territory of Azawad. Towns not shown as rebel-controlled on the map may simply not be occupied by anyone.
However, the new state of Azawad now faces a threat from another direction - the Islamist Ansar Dine militia, which
fought alongside the MNLA over the last few months (
with or without their approval). Ansar Dine is now attempting to
install strict Sharia (Islamic law) in the cities, in opposition to the MNLA's claimed desire for a secular state. An additional complication is that Ansar Dine in fact
does not support independence for Azawad, believing instead that Sharia law should be instated throughout Mali. Ansar Dine is also a Tuareg-led group.
Seen this Mali conflict map on Wikipedia?
While Political Geography Now sometimes uses free maps from
Wikipedia or other sites (after double-checking their sources), we also occasionally post our own maps to Wikipedia and
Wikimedia Commons for others to use. The first version of this particular map of the Tuareg-led rebellion in Mali was created for Wikipedia by
Orionist, but I have since taken charge of keeping it updated, with a bit of help from
Mnmazur on Wikimedia Commons (Mnmazur is not associated with Political Geography Now).